PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
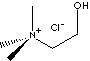
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
VITAMINS /
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Choline is a quaternary ammonium compound having a hydroxyl substituent with general formula, (CH3)3N+CH2CH2OHX- . It is a strongly basic hygroscopic amine substance distributed widely in plant and animal tissues. It is often referred to vitamin B complex. It is the basic constituent of lecithin (a group of phospholipids of the general composition CH2OR1CHOR2CH2OPO2OHR3, where R1 and R2 are fatty acids and R3 is choline) and other phospholipids. Sphingomyelin is a phospholipid consisting of choline, sphingosine, phosphoric acid, and a fatty acid. Choline prevents the deposition of fat in the liver. It is essential in normal fat and carbohydrate metabolism. It is a precursor of acetylcholine which is released at the ends of nerve fibers in the somatic and parasympathetic nervous systems. It is essential in synaptic transmission of nerve impulses. Choline is also involved in protein metabolism and transmethylation as a methylating agent. Methionine and choline are important donors of methyl groups in biochemistry. Choline is also oxidized to form betaine in methionine biosynthesis. Choline and its salts and esters are widely used in the industry of feed, agriculture, food, health care, pharmaceuticals, and biochemistry.
50.0% or 60.0% min
4.0% max
85% min ( 20 mesh)
50.0% min
2.0% max
95% min ( 20 mesh)
70.0% or 75.0% min
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
0.2% max